1 Setting up R and Rstudio
1.1 Introduction to Installing R and RStudio
1.1.1 Install R
- Install R, a free software environment for statistical computing and graphics from CRAN, the Comprehensive R Archive Network.
- Go to the CRAN website.
- At the top of the page, choose your operating system:
- Windows: Click on “Download R for Windows” and then “base”. Click on the “Download R x.x.x for Windows” link to download the installer. Run the installer and follow the instructions.
- macOS: Click on “Download R for (Mac) OS X”. Click on the
.pkgfile link to download the installer. Open the downloaded file and follow the installation instructions. - Linux: Follow the instructions for your specific Linux distribution on the CRAN page.
1.1.2 Install RStudio
- Install RStudio, an integrated development environment (IDE) for R from the RStudio website . RStudio makes R easier to use by providing a user-friendly interface and additional tools.
- Go to the RStudio Download page.
- Under “Installers for Supported Platforms”, choose your operating system:
- Windows: Click on the “RStudio-Installer.exe” link to download the installer. Run the installer and follow the instructions.
- macOS: Click on the “RStudio-Installer.dmg” link to download the installer. Open the downloaded file and follow the installation instructions.
- Linux: Click on the “RStudio-Installer.deb” link for Debian-based distributions or the “RStudio-Installer.rpm” link for RedHat-based distributions. Follow the instructions for your specific Linux distribution.
1.1.3 Update R and RStudio
1.1.3.1 Why Update?
Keeping R and RStudio up to date is important because updates often include:
- Bug fixes: Resolving known issues that might affect performance and functionality.
- New features: Adding new tools and capabilities that can make your work easier and more efficient.
- Packages: Some packages may need newer versions of R to run.
1.1.3.2 How to Update R
- Visit the CRAN website.
- Download the latest version of R for your operating system following the installation instructions provided above.
- Install the new version of R. During installation, you can choose to keep your existing packages or reinstall them after the update.
1.1.3.3 How to Update RStudio
- Open RStudio.
- Go to
Help>Check for Updates.
- If an update is available, follow the prompts to download and install the latest version.
- Alternatively, you can visit the RStudio Download page and download the latest version for your operating system, then run the installer.
1.1.4 Install Packages
Packages are collections of R functions, data, and compiled code in a well-defined format. They extend the functionality of R and are stored in repositories like CRAN. To use additional functionality in R, you often need to install and load packages.
1.1.4.1 How to Install Packages
To install a package, use the install.packages() function. For example, to install the ggplot2 package, you would run:
install.packages("ggplot2")You could also add the “dependecies = TRUE” if you want to be explicit about also installing additional packages that the package depends on.
install.packages("ggplot2", dependencies = TRUE)Once installed, you need to load the package into your R session with the library() function:
library(ggplot2)2 Work space
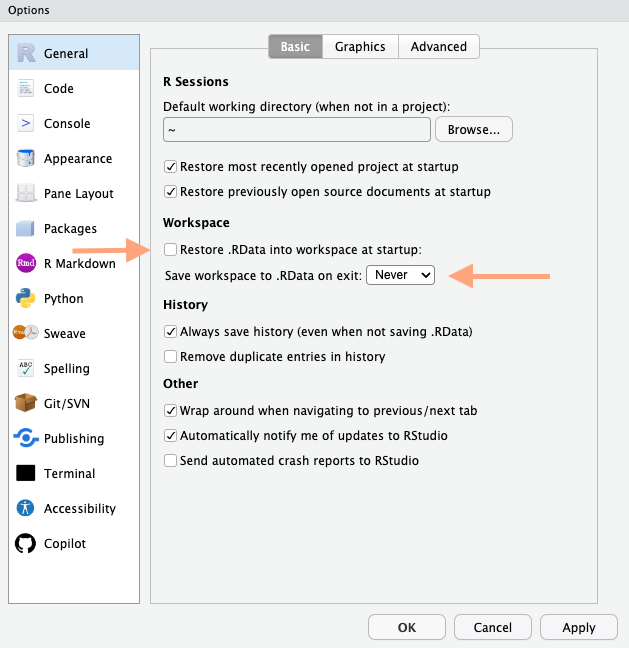
To ensure each R-session always starts fresh, with no dataset or objects loaded, ensure you uncheck the box Restore .RData and that it never asks to save the whole workspace. Go to Preferences > General. Uncheck the option Restore .RData into workspace at startup. Select Never for the option to save your workspace.
Reasons Not to Save RStudio Workspace:
- Reproducibility: Ensures scripts run consistently on any system.
- Memory Management: Prevents slow performance due to large datasets.
- Clarity and Control: Keeps the working environment clean and manageable.
- Avoiding Errors: Reduces risks of unintended variable conflicts and errors.
- Best Practices: Demonstrates that code is self-sufficient and robust.

2.0.1 Installing the tidyverse Package
install.packages("tidyverse")Then load the tidyverse package:
library(tidyverse)```2.0.2 Getting Started with R and RStudio
Once you have installed both R and RStudio, you can open RStudio and start writing R code. RStudio provides a powerful environment for coding in R with features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and an integrated console.
Here are some additional resources to help you get started: * R Documentation: Comprehensive documentation for R functions and packages. * RStudio Tutorials: Tutorials and webinars to help you learn R and RStudio.
3 Exercises
To use the exercises, you need to have a JavaScript-enabled browser.
What function loads a package that is already on your computer?
What function is used to install packages in R?
Which of the following is NOT a core package in the tidyverse?
How do you load the tidyverse package?
How do you install the tidyverse package?
4 tangentkombinationer
book https://stat545.com/index.html
Materials for teaching https://education.rstudio.com/teach/materials/
tools for teaching https://education.rstudio.com/teach/tools/
version control and git https://peerj.com/preprints/3159/ https://happygitwithr.com/big-picture
load packages recuangular data in compute something very important write rectangular data out rectangular data in make a figure save figure as pdf or png
https://datasciencebox.org/02-exploring-data
